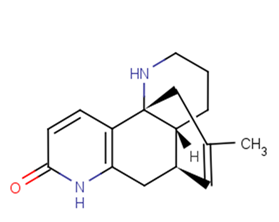
Huperzine B
CAS No. 103548-82-9
Huperzine B( —— )
Catalog No. M17768 CAS No. 103548-82-9
Huperzine-B is a efficient inhibitor of human brain AChE. Huperzine-B can enhance ognitive and protect neuro, may be potentially new drug candidates for Alzheimer's disease therapy.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 132 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 227 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 429 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 538 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 767 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameHuperzine B
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionHuperzine-B is a efficient inhibitor of human brain AChE. Huperzine-B can enhance ognitive and protect neuro, may be potentially new drug candidates for Alzheimer's disease therapy.
-
DescriptionHuperzine-B is a efficient inhibitor of human brain AChE. Huperzine-B can enhance ognitive and protect neuro, may be potentially new drug candidates for Alzheimer's disease therapy.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number103548-82-9
-
Formula Weight256.34
-
Molecular FormulaC16H20N2O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 25 mg/mL (97.53 mM)
-
SMILESCC1=CC2CC3=C(C=CC(=O)N3)C4(C1)C2CCCN4
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
ASN03576800
ASN03576800 is an inhibitor of the VP40 matrix protein.
-
Ilexhainanoside D
Ilexhainanoside D is a natural product from Periploca sepiumBge.
-
8-Oxycoptisine
8-Oxycoptisine is a natural product with Anti-inflammatory, analgesic, cooling, antihypertensive, anti-cancer



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


